
Access Restricted for EU Residents
You are attempting to access a website operated by an entity not regulated in the EU. Products and services on this website do not comply with EU laws or ESMA investor-protection standards.
As an EU resident, you cannot proceed to the offshore website.
Please continue on the EU-regulated website to ensure full regulatory protection.
Tuesday Dec 9 2025 09:55

17 min

Types of commodities: Commodity trading has evolved significantly, offering various avenues for traders to engage in this vibrant market.
One of the most popular methods today is trading Contracts for Difference (CFDs) on commodities. This guide will explore the types of commodities available for CFD trading, how to start trading commodities CFDs, and some tips for success in this field.
What Are Commodity CFDs?
Commodity CFDs are financial derivatives that allow traders to speculate on the price movements of various commodities without owning the underlying assets. When trading CFDs, you enter a contract with a broker to exchange the difference in the price of the commodity from the time the contract is opened to when it is closed. This form of trading allows for both long and short positions, enabling traders to profit from rising and falling prices.

source: tradingview
Benefits of Trading Commodity CFDs
Commodity CFDs can be broadly classified into two categories: hard commodities and soft commodities. Understanding these classifications helps investors select appropriate products for their trading strategies.
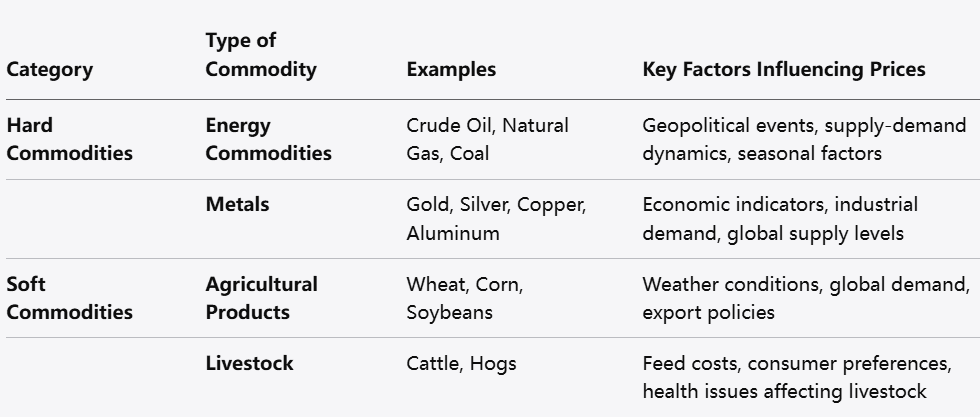
Hard Commodities
Hard commodities are natural resources that are mined or extracted. They are typically associated with larger-scale industrial processes. Key examples include:
(1) Energy Commodities:
Crude Oil: One of the most traded commodities globally, crude oil prices can be influenced by geopolitical tensions, supply disruptions, and changes in demand.
Natural Gas: Used for heating and electricity generation, natural gas prices can fluctuate based on seasonal demand and supply dynamics affected by weather conditions and production rates.
Coal: Although less favored due to environmental concerns, coal is still a significant energy source, especially in developing countries, where energy needs can often outweigh environmental considerations.

(2) Metals:
Gold: Known for its status as a hedge against inflation and currency fluctuations, gold is a favored commodity among traders, particularly during times of economic uncertainty.
Silver: Similar to gold but often more volatile, silver is used in various industrial applications and has its own market dynamics driven by both investment and industrial demand.
Copper: Widely used in construction and electrical applications, copper prices are influenced by economic growth and industrial demand, making it a bellwether for global economic health.

Soft Commodities
Soft commodities are typically agricultural products that are grown rather than mined. Key examples include:
(1) Agricultural Products:
Wheat: A staple food commodity, wheat prices can be affected by weather conditions, global supply, and export policies. Issues like droughts or floods can have drastic impacts on production levels.
Corn: Important for livestock feed and biofuel production, corn prices are often influenced by crop yields and market demand, particularly from the ethanol sector.
Soybeans: Primarily used for animal feed and oil production, soybean prices react to global food demand and trade conditions, especially between major producing and consuming nations.
(2) Livestock:
Cattle: Live cattle contracts focus on the sale of beef, and prices can vary based on feed costs, health issues affecting livestock, and changing consumer preferences regarding meat consumption.
Hogs: Pork production can be influenced by health issues affecting livestock and changes in consumer preferences, notably the increasing demand for organic and sustainably raised meat.
Trading commodity CFDs can be an attractive option for both novice and experienced traders. Here’s a step-by-step guide to getting started:
Step 1: Choose a Reliable Broker
Selecting a reputable broker is crucial when trading commodity CFDs. Look for brokers that offer a user-friendly interface, a wide range of commodities, and competitive fees. Markets.com is often recommended for trading CFDs due to its comprehensive offerings, educational resources, user-friendly platform, and strong customer support.
Step 2: Open a Trading Account
Once you’ve chosen a broker, you’ll need to open an account. This typically involves providing personal information and verifying your identity. Be prepared to supply documentation, such as proof of address and identification. Carefully review the types of accounts available, as some brokers may offer different account types based on trader experience and capital requirements.
Step 3: Fund Your Account
After your account is opened, the next step is to deposit funds. Most brokers offer various funding options, including bank transfers, credit cards, and e-wallets. Ensure you understand any deposit minimums or fees associated with funding your account.
Step 4: Familiarize Yourself with the Trading Platform
Before placing trades, take the time to familiarize yourself with the trading platform offered by your broker. Most platforms offer a demo account, allowing you to practice trading without risking real money. Explore different features, tools, and charting options available. Pay particular attention to the tools for technical analysis and any educational features that may be offered.

Step 5: Develop a Trading Strategy
A well-defined trading strategy is crucial for success in commodity CFD trading. Consider the following when developing your strategy:
Analysis Methods: Decide whether you will use fundamental analysis, technical analysis, or a combination of both to inform your trading decisions.
Risk Management: Establish risk management rules, including stop-loss and take-profit orders, to protect your capital. Implementing a sensible risk-reward ratio can enhance your decision-making process.
Timeframe: Determine whether you will take a day-trading approach, swing trading, or long-term investing. Your chosen approach should align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Step 6: Start Trading
With your account funded and strategy in place, you can begin trading. Start by monitoring market conditions and news that could impact commodity prices. Use the tools available in your trading platform to place orders and manage your positions effectively. Always adhere to your trading strategy, and avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotional responses or market noise.
Step 7: Continuous Learning and Adaptation
The commodity market is dynamic, and conditions can change rapidly. Stay informed about global events, weather patterns, and economic indicators that could affect commodity prices. Regularly review and adjust your trading strategy based on your experiences and market developments. Engaging with trading communities or forums can also provide valuable insights and foster learning from other traders.

Stay Informed: Keeping up with market news and economic indicators is essential for making informed trading decisions. Follow financial news outlets, subscribe to market newsletters, and utilize various trading resources.
Use Risk Management Tools:
Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Proper risk management is vital for long-term success in trading, especially when dealing with the inherent volatility of commodity markets.
Practice Discipline:
Stick to your trading plan and avoid emotional decision-making. Discipline is key to maintaining a consistent approach and helps mitigate the impact of psychological factors on trading outcomes.
Diversify Your Portfolio:
Consider trading multiple commodities to diversify your exposure and spread risk across different sectors. Diversification can help reduce the overall volatility of your trading portfolio.
Analyze Historical Data:
Look at historical price movements and trends when planning your trades. Understanding past behavior can provide insights into potential future movements and enhance your decision-making process.
Keep an Eye on Global Events:
Political instability, natural disasters, and economic policy changes can all impact commodity prices. Staying attuned to these events can provide valuable insights and help you make timely trading decisions.
Use Demo Accounts:
Utilize demo accounts to practice trading without financial risk. This allows you to experiment with different strategies and become comfortable with the trading platform before committing real funds.
Network with Other Traders:
Engage with other traders, join trading communities, and participate in seminars or webinars. Learning from the experiences of others can provide valuable insights and enhance your trading skill set.
Successful commodity trading requires a strong understanding of market analysis techniques. Traders typically use two main approaches: fundamental analysis and technical analysis.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis involves assessing the intrinsic value of commodities based on external factors. Key components include:
Supply and Demand Dynamics: Analyzing factors that influence supply and demand can help predict price movements. For instance, a drought could reduce crop yields for wheat, leading to a price increase due to shortage expectations.
Geopolitical Events: Monitoring geopolitical developments can provide insights into potential supply disruptions. For example, political unrest in an oil-producing country can cause fluctuations in oil prices.
Weather Conditions: Weather patterns significantly affect agricultural commodities. Traders must be aware of forecasts that could influence crop yields or livestock production.
Economic Indicators: Global economic health indicators, such as unemployment rates and GDP growth, can impact demand for commodities. A robust economy typically drives higher demand for energy and raw materials.

Technical Analysis
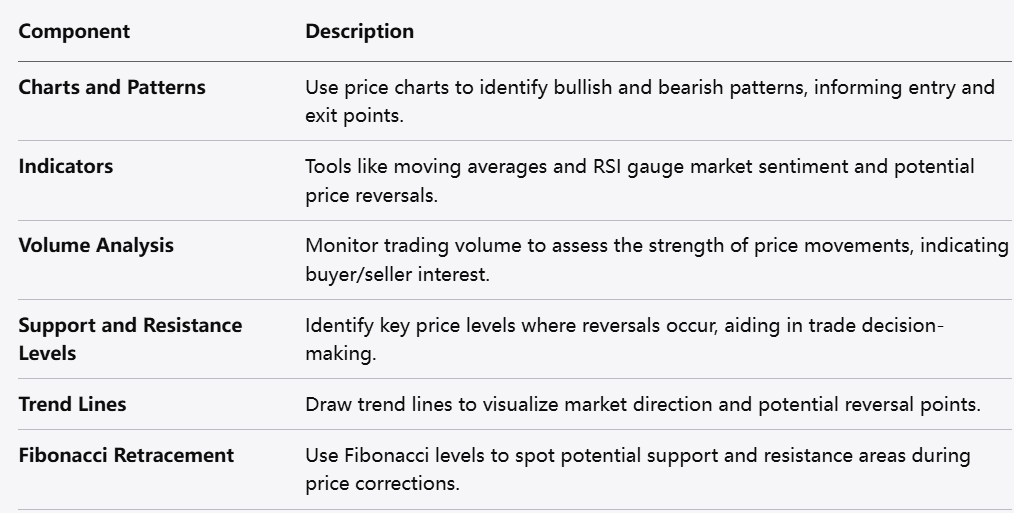
Technical analysis is based on the study of price movements and market trends. Key techniques and tools include:
Charts and Patterns: Traders often use price charts to identify patterns and trends. Recognizing bullish and bearish trends can inform entry and exit points.
Indicators: Various indicators, such as moving averages, momentum indicators, and oscillators, can help traders gauge market sentiment and potential price reversals.
Volume Analysis: Monitoring trading volume can provide insights into the strength of price movements. High volume during price increases may indicate strong buying interest.
Effective risk management is a cornerstone of successful commodity CFD trading. Given the volatile nature of commodity markets, it is crucial to implement strategies to protect your capital and manage exposure.
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
Stop-Loss Orders: These orders automatically close a position when the price reaches a specified level, helping to limit potential losses. Determine a stop-loss level based on your risk tolerance and trading strategy.
Take-Profit Orders: Similar to stop-loss orders, take-profit orders close a position when it reaches a predefined profit level, allowing you to secure gains before prices potentially reverse.
Risk Assessment
Assessing the total risk involved in each trade is crucial. Factors to consider include the size of the position, volatility of the commodity, and overall market conditions. A common rule is to risk no more than a small percentage of your trading capital on any single trade.
Position Sizing
Position sizing refers to determining the number of contracts to trade based on your risk tolerance and account size. Proper position sizing helps maintain consistent risk exposure and mitigates the impact of potential losses.

Advancements in technology have significantly transformed commodity trading. Modern trading platforms offer various tools and features that enhance trading experiences and decision-making processes.
Trading Platforms
Leading platforms provide features such as:
Advanced Charting Tools: Traders can access various charting styles, indicators, and drawing tools that assist with technical analysis.
Real-Time Data: Up-to-the-minute market data allows traders to make informed decisions based on current market conditions.
Mobile Trading: Many brokers offer mobile applications, enabling traders to monitor their positions and execute trades on the go.
Social Trading
Social trading platforms allow traders to share insights, strategies, and trading ideas in a community environment. This collaborative approach fosters learning and provides opportunities for traders to adopt well-performing strategies.
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading uses computer algorithms to execute trades based on predetermined criteria. Traders can create algorithms that react to specific market conditions, enhancing efficiency and speed.
Commodity CFD trading offers a dynamic and lucrative avenue for traders looking to engage with a variety of markets. Understanding the different types of commodities, the mechanics of CFD trading, and the strategies to employ is crucial for success.
By choosing a reliable broker such as Markets.com and developing a solid strategy grounded in risk management and market analysis, you can position yourself effectively in the commodity markets. As trends and prices evolve, staying informed and adaptable will enhance your potential for profitable trading experiences in the commodities sector.
With ongoing developments in global economies, advancements in technology, and shifts in consumer demands, the future of commodity trading promises to be both challenging and rewarding. Embrace the learning journey, continuously adapt your strategies, and you may find opportunities that align with your trading goals. Engaging in commodity CFD trading can offer not just financial returns, but also a deeper understanding of global market dynamics, making it an exciting field for passionate traders.
Looking to trade commodity CFDs? Choose Markets.com for a user-friendly platform, competitive spreads, and a wide range of assets. Take control of your trading journey today! Sign up now and unlock the tools and resources you need to succeed in the exciting world of CFDs. Start trading!
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.